
AI's ability to automate repetitive tasks and analyze vast amounts of data have the potential to revolutionize the way organizations manage their most valuable asset – their workforce. However, using AI in HR needs to be done carefully to get the most out of it and avoid any problems while following ethical rules.
As organizations navigate this uncharted territory, a comprehensive roadmap for responsible AI implementation in HR is essential. This article explores the intricacies of this process, providing a holistic framework that balances innovation with ethical considerations, fosters trust and promotes a human-centric approach to AI adoption in HR.
Understanding AI and its Applications in HR
AI technologies, such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision, have the potential to transform various HR functions, including:
-
Talent Aquisition and Recruitment: AI can streamline the recruitment process by automating resume screening, identifying top candidates, and reducing unconscious biases in hiring decisions.
-
Performance Management: AI-powered analytics can provide valuable insights into employee performance, enabling data-driven decision-making and personalized feedback loops.
-
Learning and Development: AI-driven personalized learning platforms can tailor training programs to individual needs, accelerating skill development and ensuring a future-ready workforce.
-
Employee Engagement and Retention: AI-powered sentiment analysis and predictive analytics can help identify factors contributing to employee disengagement, enabling proactive interventions and strategies to retain talent management.
-
Workforce Planning and Optimization: AI can assist in forecasting workforce needs, optimizing resource allocation, and identifying skill gaps, enabling organizations to stay agile and responsive to changing business demands.
Although AI can bring significant advantages to HR, it needs to be introduced carefully to ensure it's done in a responsible and ethical way. Not doing so could lead to unintended problems like keeping biases going, breaking privacy rules, and making employees trust the system less, which would work against the goals AI is supposed to help with.
The Pillars of Responsible AI Implementation in HR
Developing a responsible AI implementation strategy in HR requires a multifaceted approach that addresses various ethical, legal, and organizational considerations. This road is built on four fundamental pillars:
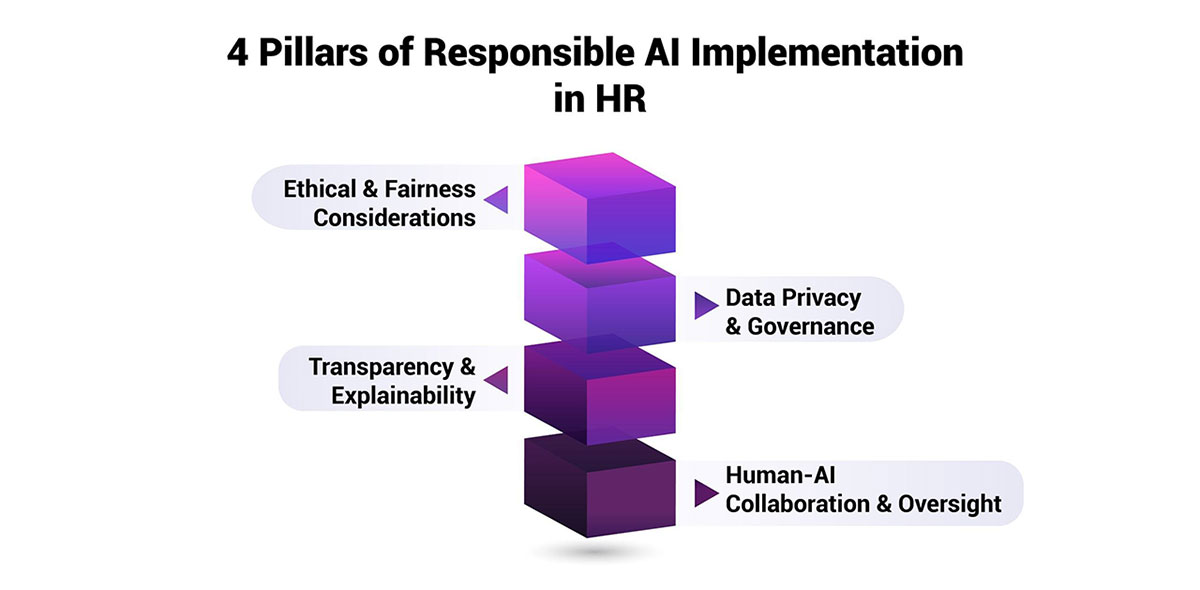
Let's explore each of these pillars in detail:
-
Pillar 1: Ethical and Fairness Considerations
AI systems are only as unbiased as the data and algorithms they are trained on. Unconscious biases can creep into AI models, leading to discriminatory outcomes that undermine diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) efforts within organizations. To mitigate these risks, a responsible AI implementation strategy must prioritize ethical and fairness considerations throughout the AI life.
-
Pillar 2: Data Privacy and Governance
The responsible implementation of AI in HR heavily relies on the ethical handling and government of employee data. Organizations must prioritize data privacy and ensure compliance with relevant regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), to maintain employee trust and avoid legal repercussions.
-
Pillar 3: Transparency and Explainability
AI systems, particularly those based on complex machine learning models, can often be perceived as "black boxes," making it challenging to understand how decisions are made. This lack of transparency can erodes employee trust and hinders the adoption of AI in HR. Responsible AI implementation demands transparency and explainability to ensure fairness, accountability, and stakeholder buy-in.
-
Pillar 4: Human-AI Collaboration and Oversight
While AI can augment and enhance HR processes, it should not replace human decision-making entirely. A responsible AI implementation strategy recognizes the strengths and limitations of both AI and human intelligence, fostering a collaborative approach where humans remain in control and provide oversight.
Building a Culture of Responsible AI in HR
Key strategies for building a culture of responsible AI in HR include:

-
Leadership Buy-in and Commitment: Responsible AI implementation must be championed by organizational leaders, who should demonstrate visible commitment to ethical AI practices. Leaders should actively participate in setting the tone, allocating resources, and promoting a culture of accountability and transparency around AI systems in HR.
-
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Foster cross-functional collaboration between HR professionals, talent management practitioner, data scientists, legal experts, ethics advisors, and employee representatives. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that different perspectives and expertise are incorporated into the development and development of AI systems, promoting a holistic and balanced approach.
-
Ethical Training and Awareness: Create thorough training programs to teach people about the ethical considerations of AI in HR and the principles of responsible AI. These training efforts should be designed for different groups like HR staff, managers, and employees, so everyone understands and agrees on how AI should be used ethically.
-
Continuous Dialogue and Feedback Loops: Set up open channels for ongoing conversation and feedback loops with employees. Encourage employees to express their concerns, share their experiences, and give input about AI systems.This fosters trust transparency and helps identify potential issues or areas for improvement.
-
Ethical AI Ambassadors: Identify and empower "ethical AI ambassadors" within the organization – individuals who champion responsible AI practices and serve as role models for others. These ambassadors can help drive cultural change, share best practices and ensure that ethical considerations are at the forefront of AI adoption in HR.
-
Reward and Recognition Systems: Align reward and recognition systems with responsible AI practices. Celebrate and recognize individuals and teams who demonstrate a commitment to ethical AI principles, foster transparency, and prioritize the responsible implementation of AI in HR.
Overcoming Challenges and Building Trust
Despite the immense potential of AI in HR, its responsible implementation may face various challenges and barriers. Overcoming these challenges and building trust among stakeholders is crucial for the successful adoption and sustained impact of AI in HR.
Common challenges in responsible AI implementation include:

-
Resistance to Change: Some employees or managers may be resistant to the adoption of AI in HR processes, fearing job displacement, loss of control, or a perceived threat to their expertise. Addressing these concerns through open communication, education, and clear demonstrations of the benefits of AI-human collaboration is essential.
-
Data Quality and Availability: AI systems heavily rely on high-quality and diverse data, which may not always be readily available or easily accessible. Organizations may need to invest in data collection, cleaning, and integration efforts to ensure that AI models are trained on reliable and representative data.
-
Ethical Dilemmas and Trade-offs: Responsible AI implementation may present ethical dilemmas and trade-offs, such as balancing the need for transparency with the protection of proprietary algorithms or navigating conflicts between fairness and business objectives. Developing clear ethical frameworks and decision-making processes can help navigate these complexities.
-
Regulatory Compliance: As AI adoption increases, so do the regulatory requirements and guidelines around its responsible use. Keeping up with evolving regulations and ensuring compliance can be a significant challenge, particularly for organizations operating across multiple jurisdictions.
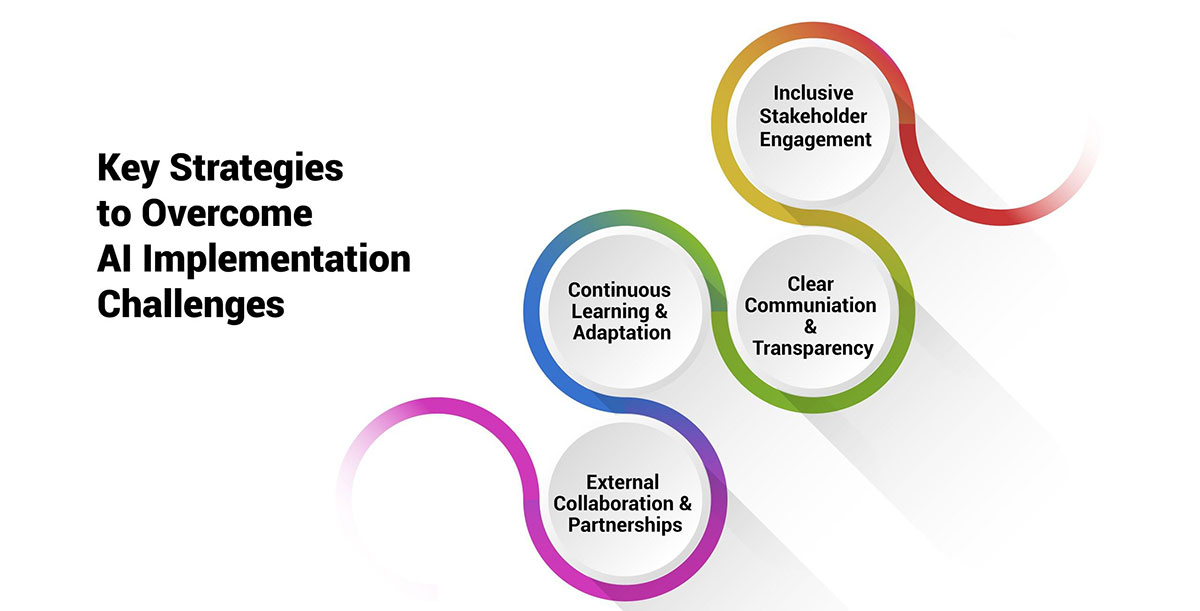
To overcome these challenges and build trust among stakeholders, organizations should adopt a proactive and transparent approach. Key strategies include:
-
Inclusive Stakeholder Engagement: Actively engage with employees, employee representatives, regulatory bodies, and other stakeholders throughout the responsible AI implementation process. Seek their input, address their concerns, and involve them in decision-making processes to foster a sense of ownership and trust.
-
Clear Communication and Transparency: Communicate openly and transparently about the organization's responsible AI initiatives, policies, and practices. Provide regular updates, share success stories, and be transparent about challenges and setbacks, demonstrating a commitment to continuous improvement.
-
Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Encourage a culture of continuous learning and adaptation within the organization. Stay updated on emerging best practices, regulatory developments, and technological advancements in the field of responsible AI, and be prepared to adapt strategies and practices accordingly.
-
External Collaboration and Partnerships: Collaborate with industry associations, academic institutions, and other organizations to share knowledge, learn from best practices, and collectively advance the responsible implementation of AI in HR.
Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement
Implementing responsible AI practices in HR is not a one-time endeavor but an ongoing journey that requires continuous monitoring, evaluation, and improvement. Measuring the success of responsible AI initiatives is crucial to identify areas for enhancement, demonstrate the positive impact on organizational outcomes, and maintain stakeholder trust and support.
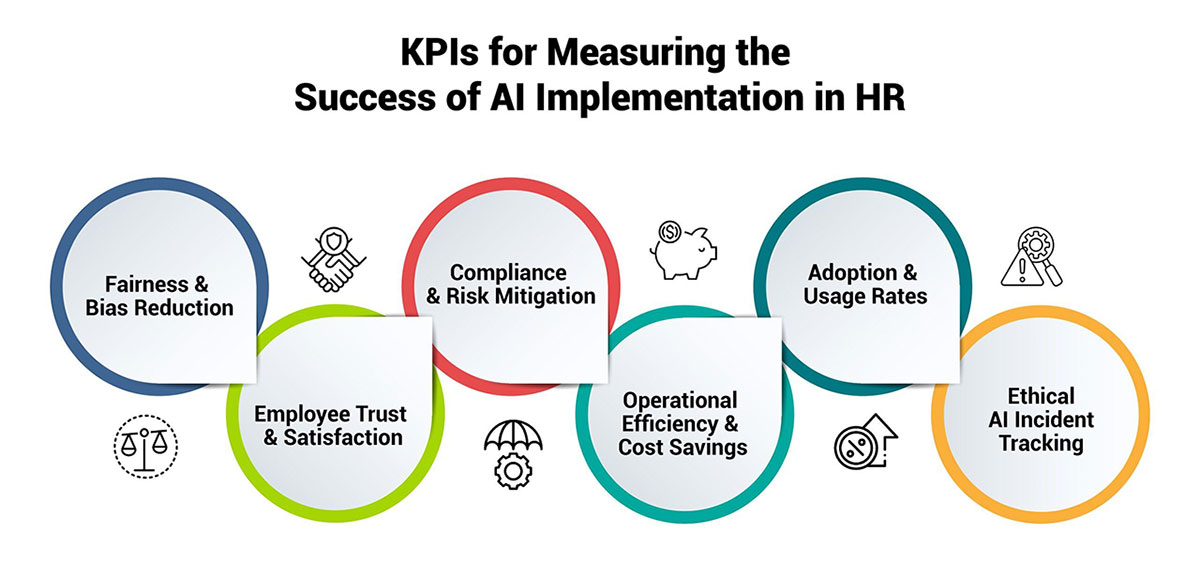
Key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics for measuring the success of responsible AI implementation in HR may include:
-
Fairness and Bias Reduction: Metrics related to the reduction of bias and discrimination in HR processes, such as equal opportunity hiring rates, pay equity, and promotion rates across different demographic groups.
-
Employee Trust and Satisfaction: Surveys and feedback mechanisms to measure employee trust in AI systems, satisfaction with AI-driven decisions, and overall perceptions of the organization's commitment to responsible AI practices.
-
Compliance and Risk Mitigation: Metrics related to compliance with relevant regulations, such as data privacy laws and anti-discrimination policies, as well as the mitigation of legal and reputational risks associated with AI misuse or unethical practices.
-
Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings: Quantifiable metrics related to the operational efficiencies and cost savings achieved through the responsible implementation of AI in HR processes, such as reduced time-to-hire, improved employee retention, and optimized resource allocation.
-
Adoption and Usage Rates: Metrics that track the adoption and usage rates of AI systems among HR professionals and managers, indicating the level of buy-in and acceptance of these technologies.
-
Ethical AI Incident Tracking: A system for tracking and documenting incidents or concerns related to the ethical or responsible use of AI in HR, along with the actions taken to address them.
Continuous improvement should be a core principle in the responsible AI journey. Organizations should regularly review and analyze these metrics, identify areas for enhancement, and implement corrective actions or process improvements.
Conclusion
The integration of AI in HR presents a transformative opportunity for organizations to enhance their workforce management practices, drive operational efficiencies, and gain a competitive edge. However, the responsible implementation of AI in HR is paramount to ensure that these benefits are realized while upholding ethical principles, fostering trust, and prioritizing employee well-being.
It is important to recognize that responsible AI implementation is an ongoing journey, requiring continuous monitoring, evaluation, and improvement. By measuring success, embracing a mindset of continuous learning, and collaborating with external experts and stakeholders, organizations can stay ahead of the curve and position themselves as leaders in the ethical and responsible adoption of AI technologies.
As AI continues to reshape the future of work, organizations that prioritize responsible AI implementation in HR will not only gain a competitive advantage but also contribute to the creation of fair, inclusive, and future-ready workplaces. By striking the right balance between innovation and ethical considerations, these organizations will pave the way for a harmonious coexistence of human intelligence and artificial intelligence, fostering a workforce that is empowered, engaged, and equipped to thrive in the digital age.







