
One of the most significant assets of any company is the people performing various job roles. Success may begin with a unique idea or system of processes, but it grows and is supported by physical human beings learning a skill or trade and perfecting an operation. Strategic talent management can either drive or hinder business growth. From conducting HR due diligence to setting up HR management systems and leading executive recruitment, a well-structured approach makes a significant difference in securing long-term success.
The business strategy needed to account for human assets must adapt over time. To secure sustainable growth, companies looking to remain competitive must attract, develop, and retain top talent. Yet, too often, talent acquisition is treated as a secondary HR function rather than a core business strategy. The reality is that people, alongside market positioning, finance, and business processes, form the backbone of long-term business viability.
Below is a strategic HR framework designed to help businesses not only attract top talent but also retain them over the long term and develop their value in alignment with future growth.
Most global businesses leverage HR on two separate levels:

Corporate Level: HR provides support for staff budgeting, process automation, and cultivating a culture of respect to enhance productivity.
Individual Employee Management: HR develops a robust employee lifecycle, including:
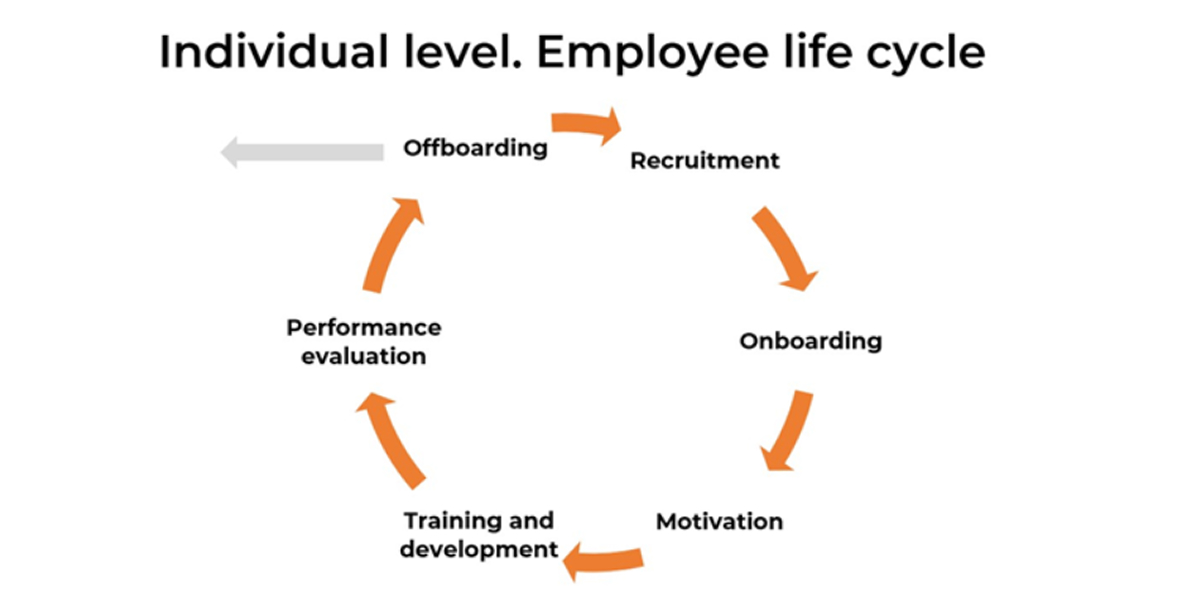
Combining these two HR scopes ensures that current employee concerns are addressed while leadership is equipped with data for strategic future planning.
There is no universal HR strategy that solves every business challenge. The strategy must align with the business model, industry, and growth objectives.
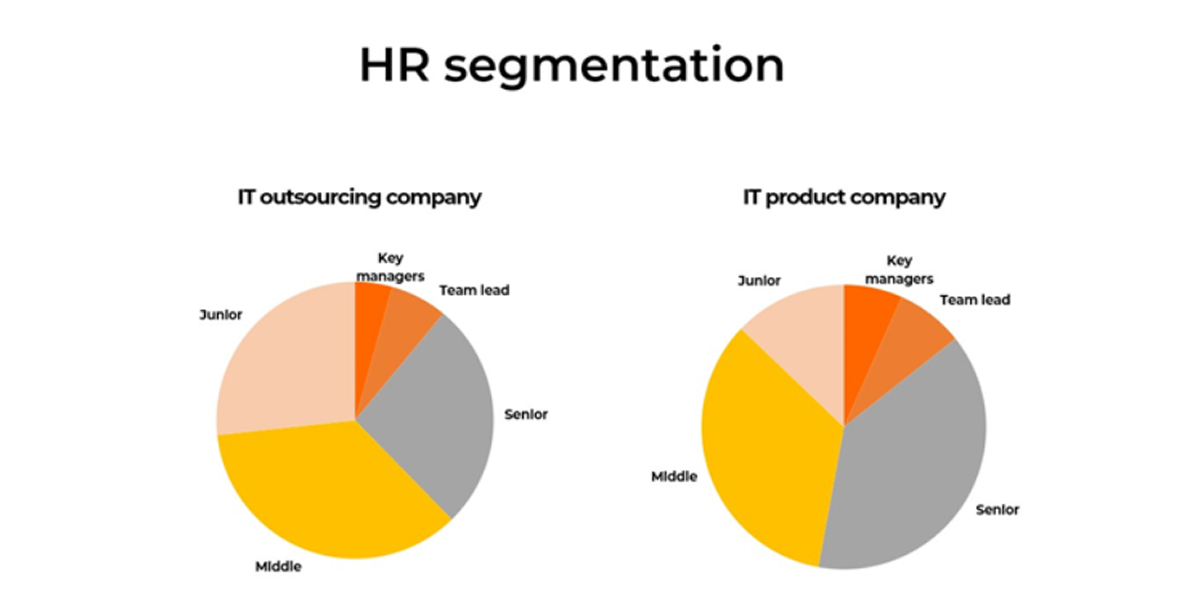
For example:
HR priorities must be refined to meet the unique needs of the organization. The strategy should also account for employees with specialized knowledge developed over years of engagement, forming a significant part of the operational structure.
Employee wages and expenses comprise a significant portion of a company’s budget. When structuring an HR strategy, it must be translated into an understandable financial model. Salaries often make up less than 40% of total personnel costs, which also include:
Personnel costs should rise proportionally with revenue rather than at the same rate. Two key financial metrics help in optimizing workflows and expenses:
Labor Productivity: Revenue generated per employee annually.
Personnel Profitability: Revenue earned for every unit spent on human assets.
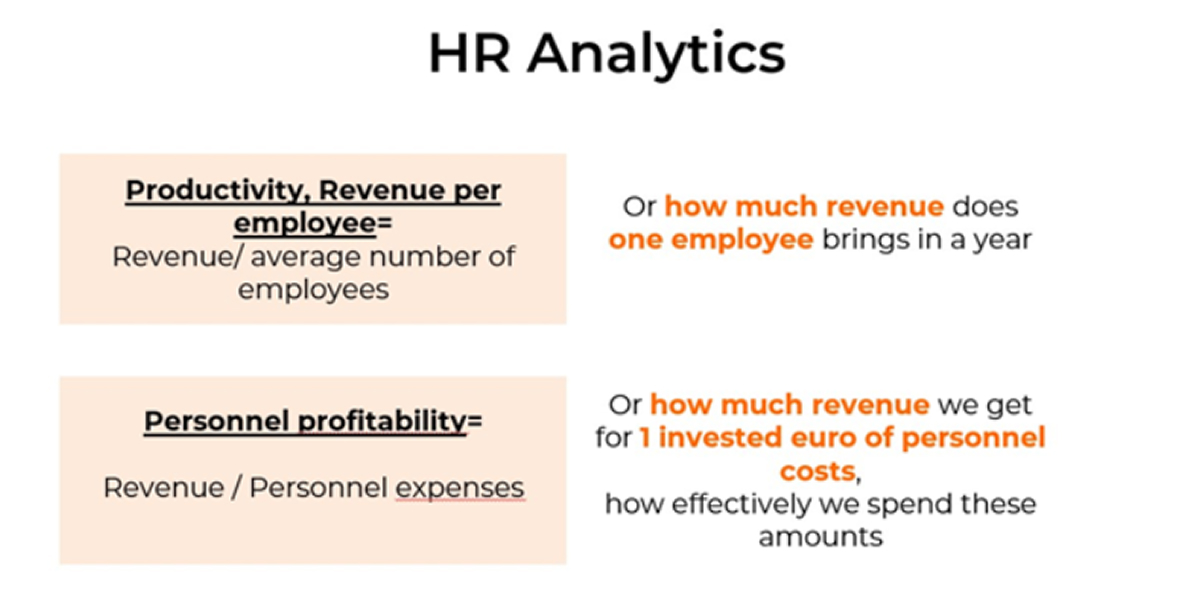
Benchmarking these metrics helps maintain a competitive advantage without compromising efficiency.
Top management and executive board members must be incentivized for operational continuity. Compensation typically includes:
Fixed salary (50-60% of total compensation)
Variable bonuses (up to 50%), tied to measurable business outcomes
KPI-based bonuses rewarding performance
Common incentive models include:
Small Executive Pools: 1-7% of company shares distributed among a small group of managers.
Broad Employee Participation: Stock options offered to employees at different levels.
Aligning compensation with business goals ensures executives are motivated to drive company success.
Even the most capable in-house HR teams may require external expertise. Industry specialists can provide:
External experts ensure businesses remain future-ready, allowing internal teams to focus on growth rather than crisis management.
HR management now leverages technology for tracking workforce metrics, including:
AI and automation streamline reporting and decision-making but must be safeguarded with security measures to protect private data.
A strong corporate culture enhances employee engagement and retention. Effective cultural initiatives include:
An authentic corporate culture strengthens employee loyalty, productivity, and customer perception of the brand.
A Smart Long-Term Talent Strategy
Hiring students and young professionals provides several advantages:
Integrating younger talent into leadership pipelines fosters long-term business stability.
A sustainable HR strategy must be built on future resilience. Effective talent management doesn’t just support business success—it actively drives it. Long-term profitability requires integrating HR into the broader business vision, ensuring that talent remains a cornerstone of growth and competitiveness.
Veronika Baranova is an experienced HR professional with over 15 years of experience in startups and large enterprises across IT, banking, telecommunications and manufacturing. She specializes in HR analytics, talent management, and workforce optimization, aligning HR strategies with business goals. Currently an HR Manager at Zubr Capital, she supports portfolio companies in building effective HR systems and executive recruitment. With expertise in HR due diligence, assessing ESG policies, compensation structuring, and performance management, Veronika is passionate about integrating data-driven HR solutions to drive company profitability and growth. She holds a degree in political economy and has completed multiple leadership and strategic HR training programs.

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Please enter the License Number/Unique Credential Code of the certificant. Results will be displayed if the person holds an active credential from TMI.