
A PESTLE analysis provides a framework for evaluating the key external environmental factors that affect an organization's activities in specific industries or regions. When applied to human resources (HR) planning and strategy, it is a useful tool for assessing how the macro environment impacts both current and future workforce management practices. In this article, we will explore how HR professionals can use the PESTLE method to proactively shape HR strategies that align with business objectives amid changing outside conditions.
PESTLE is an acronym that stands for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal and Environmental factors. It is a framework used to scan the organization's external macroenvironment and understand what external forces could possibly affect its activity, planning and, eventually, its strategy.
A PESTLE analysis offers a comprehensive overview of the external environment in which an organization operates, covering political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors. It is a situational analysis of variables that can possibly affect strategic decisions of organizations.
By utilizing the PESTLE method and applying it specifically to human resources concerns, HR leaders can gain valuable insights for developing strategic workforce plans, policies, and programs. Let's examine each of the elements and how they relate to driving effective HR decisions:
Changes in government policies and legislation can significantly impact human resource strategies and planning. Conducting a PESTLE analysis of political factors allows HR professionals to stay informed of shifting priorities and anticipate potential regulatory changes.
For example, a new government may pass reforms to minimum wage laws that affect compensation budgets. Analyzing the political landscape helps HR determine when such changes may occur so the department can begin adjusting budgets, job descriptions, and salary bands in advance to ensure swift compliance.
Monitoring election cycles and platforms of different political parties can also provide insight into future policy directions relating to employment standards. For instance, certain groups may promote expanding maternal or paternal leave policies. Evaluating this as a political factor in PESTLE permits HR to estimate timing and draft policy language for when new legislation comes into effect. Staying aware of political currents maintains the organization's adaptability to macro changes outside its control.
The economic environment profoundly influences strategies for staffing and resource allocation. Economic indicators like gross domestic product, inflation, unemployment, and interest rates all impact organizational budgets and forecasting. When assessing economic factors through PESTLE, HR can understand implications for wages, benefits, recruiting needs and turnover. For example, during an economic recession hiring freezes may be required while in recovery expanded recruitment is warranted.
Analyzing historical data on economic cycles permits informed scenario planning to optimize workforce levels based on anticipated business productivity or demand under varying conditions. Incorporating economic forecasts keeps resourcing aligned with projected performance.
Similarly, recognizing future risks like changing consumer trends due to rising living costs facilitates proactive career transition support or retraining programs for at-risk roles. Over time, consistent PESTLE monitoring captures emerging economic shifts like variable GDP contributions across industries, directing recruitment toward growing market sectors.
Societal shifts in demographics, lifestyle preferences, and cultural norms directly affect the labor supply and talent demands across functions. Evaluating social factors through PESTLE allows HR to identify generational characteristics and address multigenerational needs accordingly.
For instance, flexible work-life balance policies may attract or retain young professionals prioritizing wellbeing. In addition, understanding mobility patterns supports strategic campus recruiting near population concentrations.
Monitoring societal trends also reveals diversity gaps to target through inclusive hiring practices promoting representation. Engaging multiple demographic groups requires consideration for various accessibility requirements in all facets of employment from application portals to workplace facilities.
Adopting a diversity, equity and inclusion lens in PESTLE highlights such aspects for proactive action strengthening the employer value proposition. Analyzing social media insights further guides empathetic employment branding resonance testing across subsectors.
Emerging technologies continually transform operational processes and occupational skills profiles. Incorporating technology considerations into PESTLE enables HR to identify viable tools optimizing workflows while future-proofing the workforce. For example, reviewing industrial automation advancements signals reskilling needs alongside recruiting profiles emphasizing in-demand technical abilities.
PESTLE also helps determine strategic technology investments enhancing the employee experience, such as leveraging analytics dashboards facilitating data-driven decision making. Tracking scientific publications and patent activity aids forecasting of innovative niches to pioneeringly position in.
Staying apprised of technology diffusion curves from research to early adoption assesses timeline urgency for responsive talent strategies, learning infrastructures, and change management supports. Frequent PESTLE review maintains organizational agility leveraging advantages while mitigating threats from disruption.
Ensuring compliance with employment, health and safety legislation as well as contractual obligations represents a significant legal function for HR. Conducting PESTLE analysis of the legal landscape keeps teams informed of shifting rules and policies. This helps identify potential audit areas and risks for mitigation in advance. For instance, privacy law reforms may necessitate employee communication and data access protocol updates.
Monitoring legislative committees and court dockets for workplace law cases signals when new regulations or legal precedents require timely policy adjustments. Maintaining abreast of the compliance environment through PESTLE can also support regulatory affairs by informing lobbying or public commentary stances.
Evaluation of jurisdictional variations supports multi-location employers tailoring fair practices suiting diverse contexts while securing standard protections organization-wide. Proactive legal risk assessment further strengthens. HR defense preparedness and litigation management capabilities.
The physical environment and community element affect all operations today due to increasing sustainability responsibilities. Incorporating ecological considerations into PESTLE allows HR to implement supports balancing business needs with responsible stewardship. Initiatives can involve establishing remote work to reduce environmental impacts or commuting as well as instituting green teams driving recycling across facilities.
Consulting environmental advocacy networks and following Natural Step framework adaptations identifies impactful pollution prevention investments for lower carbon footprints. Promoting wellness also encompasses community investment volunteering benefiting surrounding areas.
Monitoring conservation regulations signals requisite compliance training or potentially advantageous subsidies through innovation. Analyzing the environmental factor empowers HR championing social commitments strengthening employer ethos and competitive advantage in attracting conscious talent.
To maximize the value of PESTLE for strategic HR planning and workforce management, here are the basic steps to conduct such an analysis:
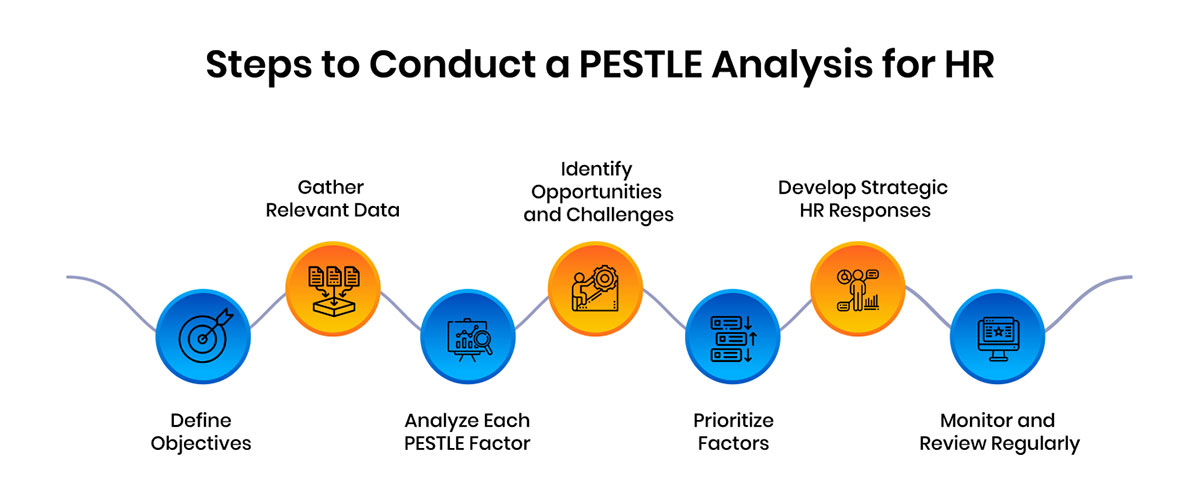
The initial step is to clearly define the aim and scope of the PESTLE analysis. For example, if the organization is looking to expand operations internationally, the PESTLE analysis could aim to evaluate how external environmental factors impact global workforce planning and management.
Alternatively, if the focus is on improving employee engagement, the analysis may seek to examine macro trends affecting staff motivation and retention. Narrowing down the specific HR priorities helps maintain analytical rigor and eventual implementation of recommendations.
Once objectives are outlined, pertinent data is compiled across the six fronts. For the political dimension, reports from trade bodies on impending labor code revisions are referred to. On the economic front, forecasts of national productivity and unemployment indices from investment banks provide demand-supply insights. For social analysis, employee surveys and census data detailing demographic shifts are reviewed.
Regarding technology, industry studies tracking automation adoption and skills requirements are analyzed. On the legal front, alerts from employment compliance portals about changing compliance burdens are noted. Lastly, for the environment, sector benchmarks on carbon footprint reduction are factored in. Gathering information from diverse yet credible sources present a balanced perspective.
Each collated input is then examined minutely to deduce current and potential implications for HR priorities. Political changes signaling wage inflation may necessitate compensation reviews while economic slides could impact training spends. Social transformations revealing aging work populations may prompt health benefit enhancements or redesign of medical leave.
Technological leaps in cognitive automation may necessitate reskilling or career transition support. Evolving legal liabilities can increase the need for policies on anti-harassment or data privacy. Environmental stewardship goals may call for hiring freeze exemptions for “green skills” or transition assistance programs. A holistic yet discerning study of every factor is vital.
Upon comprehensive analysis, the external audit is distilled to spotlight opportunities and challenges for talent optimization. Political moves improving employer branding could benefit recruitment as growing remote working norms allow wider talent pools. Yet economic uncertainty may delay performance reviews.
Social equity mandates present an opportunity to strengthen inclusion whereas demographic transitions require revised learning curricula. While technological disruption compels upskilling, it likewise breeds new jobs. Compliance bottlenecks can be converted to stronger policy frameworks and environment preservation goals offer a value proposition for candidates.
Next, influences significantly impacting personnel administration are prioritized based on urgency, complexity and scale of implications. Political reforms immediately reengineering work contracts may rank higher than emerging environmental directives years away. Economic swings severely curtailing new-joiner intake deserve precedence over long-term social evolutions. This allows for sequential mitigation of disruption and optimized utilization of budget and bandwidth.
From here, targeted action plans are formulated to capitalize on opportunities and proactively address risks. To tackle skills obsolescence due to technology, lifelong learning programs integrating internal and external resources may be conceptualized.
Where compliance challenges emerge, upgraded policy communications and training could minimize non-conformance. As demographics evolve, diverse recruiting channels and mentoring initiatives build an equitable workforce. Regular reviewing and upgrading safeguards preparedness amid dynamic scenarios.
The analysis remains incomplete without periodic reassessment and alteration. Environmental trajectories continuously change, necessitating real-time inputs. Labor codes or economic charts updated quarterly require review. Employee opinion polls provide changing perspectives. By instituting a 6-monthly cycle, the PESTLE integrates emergent intelligence to bolster strategic foresight. Flexibility future-proofs HR strategies for resilient organizational navigation.
In conclusion, the PESTLE framework provides a bird's-eye view of environmental factors critical to consider while shaping HR roadmaps and policies cementing an organization's competitive position. Its structured, contextual analysis fosters dynamic, future-proof workforce strategies driving sustainable success.

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Please enter the License Number/Unique Credential Code of the certificant. Results will be displayed if the person holds an active credential from TMI.