
The human resources department plays a pivotal role in achieving organizational goals by ensuring the company has the right people with the right skills. To effectively manage human capital assets, HR needs a strategy that aligns workforce planning with business objectives.
An HR strategy acts as a roadmap for managing people-related practices from recruitment to performance management. By creating an impactful HR strategy, organizations can enhance productivity, drive innovation, foster employee engagement, and develop a positive work environment.
In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss how to develop an effective HR Strategy and provide examples of HR strategy initiatives implemented successfully. Keep reading to learn the step-by-step process for developing your own impactful HR strategy.
What is an HR Strategy?
An HR strategy is a comprehensive plan for managing an organization's human capital to support its goals. It focuses HR activities around recruiting, developing, and retaining employees with the capabilities required to execute business strategies.
Some key elements of an effective HR strategy include:
-
Analyzing internal and external factors impacting the company and workforce.
-
Aligning people's practices with short and long-term business objectives.
-
Developing policies and processes for acquiring, engaging, and developing talent.
-
Establishing metrics to measure HR performance and contributions to business outcomes.
-
Creating programs that attract, motivate, and retain top performers.
-
Ensuring compliance with employment laws and standards.
By integrating these facets, an HR strategy serves as a guiding framework for all people-related decisions and initiatives within the organization.
Why is an HR Strategy Important?
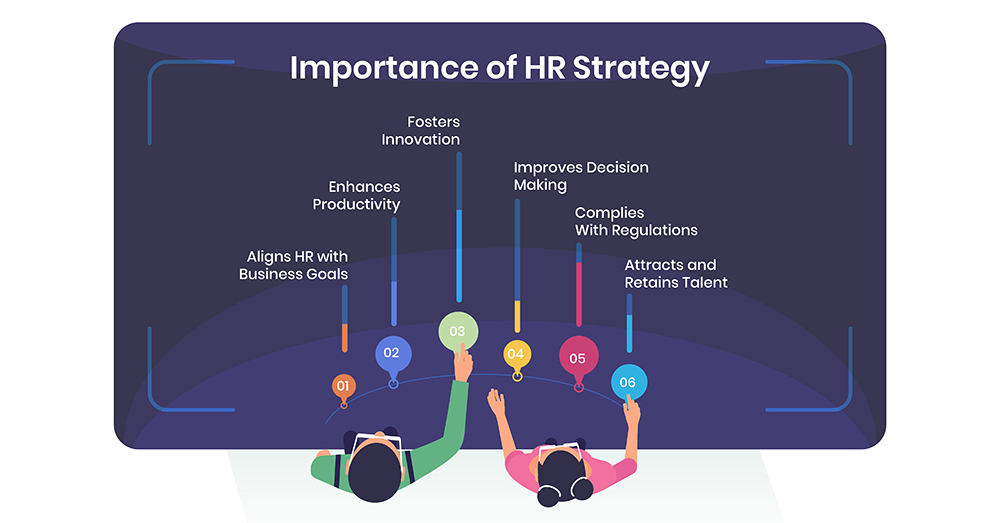
Developing an impactful HR strategy is crucial for several reasons:
-
Aligns HR With Business Goals
An HR strategy syncs recruitment, performance management, learning and development, compensation, and other HR functions around key business priorities. This helps attract candidates with the capabilities needed and retains employees committed to their goals.
-
Enhances Productivity
Strategic people practices increase employees' knowledge, skills, engagement and motivation levels. Empowered individuals can perform at their best and collaboratively drive higher output.
-
Fosters Innovation
Progressive HR plans establish a culture where individuals freely contribute ideas, take measured risks and have autonomy over some decisions. This stimulates new solutions and improves work processes.
-
Improves Decision Making
Data-driven insights from HR metrics aid fact-based conversations and people investments. Leaders can understand which initiatives truly impact performance and where to optimally allocate resources.
-
Complies With Regulations
An HR strategy demonstrates the function proactively considers compliance rather than reacting to changes. This protects brand reputation and mitigates risks of non-adherence penalties.
-
Attracts and Retains Talent
Progressive people philosophies help candidates and staff envision engaging work and development opportunities. Companies with HR strategies have competitive advantages in talent wars.
Developing an HR Strategy: Framework
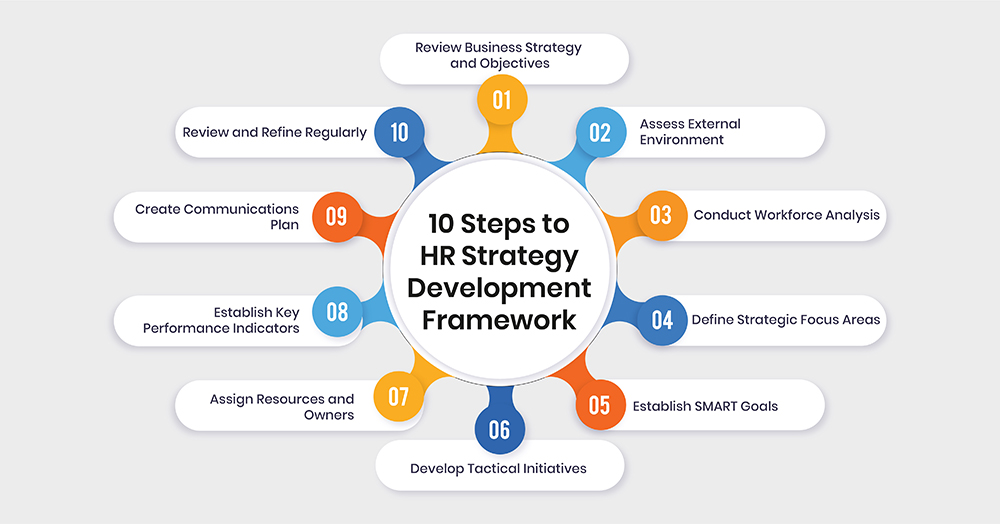
To formulate an impactful HR strategy, follow this step-by-step framework:
-
Review Business Strategy and Objectives : Start by analyzing your company's vision, mission, goals, key activities, target markets and competitors. Understand priority focus areas and challenges the business strategy aims to resolve.
-
Assess External Environment : Evaluate factors like emerging technologies, demographic shifts, economic conditions, industry trends, regulations and competition impacting your workforce.
-
Conduct Workforce Analysis : Assess employee numbers, roles, skills, performance levels, attrition and engagement scores through surveys. Identify skill gaps hampering work.
-
Define Strategic Focus Areas : Prioritize 2-4 people management domains requiring attention, like learning, culture, diversity or talent acquisition. Choose areas supporting business needs.
-
Establish SMART Goals: Create 2-4 Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant and Time-bound objectives for each focus area concluded in the previous step.
-
Assign Resources and Owners : Allocate budgets and designate leaders accountable for implementing each initiative within set timelines.
-
Establish Key Performance Indicators : Choose metrics to quantify the success of goals and initiatives periodically, like employee satisfaction rates.
-
Create Communications Plan : Develop sessions to socialize the HR strategy among staff and gain buy-ins from priority stakeholders.
-
Review and Refine Regularly : Evaluate results and refine or replace underperforming tactics based on shifting realities every 6-12 months.
This prepares a comprehensive HR strategy addressing current pain points and future opportunities to proactively support business plans. The next step is implementation.
HR Strategy Examples
But what constitutes successful strategic HR in practice? Let's explore examples of companies excelling in people management:
-
Google's Talent Philosophy: Google hires using rigorous assessments evaluating expertise, Problem-solving and Cultural fit. Features like flexible work hours, constant skills training and results-only work environments retain top talent globally.
-
Zappos' Unique Company Culture : Zappos emphasizes an enjoyable workplace through initiatives like weekly social gatherings and voluntary relocation allowances. New hires undergo intense culture immersion fostering commitment to service excellence.
-
Toyota's Approach to Employee Engagement : Toyota follows a culture of continuous improvement through recommendations. Staffers freely suggest work enhancements and even lead quality improvement projects. This stimulates innovations while boosting morale.
-
HubSpot's Focus on Learning and Development: Hubspot offers reimbursement for external courses, certifications and conferences. Employees advance skills through in-house training, collaborative projects and mentorship programs. Retention increases as a result.
-
Netflix's Unorthodox Compensation Plans : Instead of annual appraisals, Netflix focuses discussions on performance and future goals every quarter. Variable pay rewards for taking smart risks and exhibiting strategic leadership qualities.
These organizations connect HR to business aims like Google and build cohesive cultures exemplified by Zappos. HR strategies contribute to their growth, productivity and reputation as employers of choice.
Case Study: HR Strategy at EY
Ernst & Young (EY) is a leading professional services firm providing assurance, tax, strategy, transaction and consulting services to clients around the world. However, in recent years the firm found itself facing intense competition for the most in-demand skills from other professional services firms as well as technology companies. To differentiate itself from competitors and continue attracting top talent, EY's HR function recognized the need to more closely align its strategies and practices with the company's business priorities through strategic workforce management.
The objectives of EY's HR strategy were twofold. Firstly, EY aimed to develop and maintain highly specialized skills and expertise across all of its geographic regions to serve the diverse and sophisticated needs of global clients. Rapid changes in digital technologies were transforming entire industries, and clients were increasingly looking to EY for guidance on how to successfully adopt new technologies to gain competitive advantages. This meant EY professionals needed expertise not just in traditional areas like accounting and consulting but also in emerging domains like data analytics, artificial intelligence, cybersecurity and more. The speed at which these new technologies were evolving also placed a premium on employees' ability to quickly learn and apply new skills.
Secondly, EY had ambitious growth targets to boost its revenues and market share exponentially over the next five years. Sustaining such high-pace growth would require a substantial increase in headcount across roles and levels. EY's HR function recognized that having the right talent acquisition and development strategies in place would be critical to feeding the organization with the caliber of skills needed to seize growth opportunities while maintaining service quality. Failing to deliver on specialized skills and growth targets risked damaging EY's reputation as an employer of choice.
With these challenges in mind, EY's senior leadership team mandated HR to develop a new global workforce strategy aligned with the company's strategic priorities. The resulting HR strategy focused on three key pillars:
-
Pillar 1 - Reskilling the Existing Workforce
Rather than always looking externally for new hires, EY emphasized reskilling its existing talent pool where possible. The firm launched an extensive suite of online and blended learning programs covering technical skills in high-growth areas as well as soft skills like collaboration, communication and change leadership. Digital and AI-enabled tools were used to personalize learning paths for individual employees based on their roles, strengths and goals. Partnership with top universities also provided employees access to credits for degree and certificate programs in specialty domains.
To encourage participation, managers integrated skilling goals into performance management while HR incentivized learning through recognition and reward programs. Reskilling metrics formed part of business unit leaders' key performance indicators to hold them accountable for developing talent. By proactively upskilling from within, EY retained existing talent, organizational knowledge and avoided higher recruitment and onboarding costs associated with external hires.
-
Pillar 2 - Attracting Specialized Early Career Talent
EY revamped its graduate recruitment process to target specialized skill profiles aligned with firm strategy through tailored marketing campaigns, hiring events and campus engagement programs. The firm launched scholarship programs in partnership with universities to attract students studying domains of strategic importance while also funding reskilling bootcamps for non-traditional candidates like mid-career professionals making industry switches.
Aggressive campus branding, networking opportunities and rotational internship programs further strengthened EY's employer value proposition to attract a steady pipeline of future-ready talent. Advanced assessment techniques during recruitment shortlisted candidates with high learning agility. Lateraling and poaching of specialized professionals from competitors using competitive retention packages supplemented this pipeline. EY thus ensured availability of skills needed to develop niche expertise and expand into new service offerings.
-
Pillar 3 - Global Resourcing and Deployment
A newly formed Global Resourcing and Deployment team used robust workforce analytics tools and processes to balance demand for skills against supply on a continuous basis across every geography, service line and project stage. By maintaining a real-time view of resourcing requirements and available talent pools worldwide, the team seamlessly redeployed employees from project to project or geography to geography to minimize under-/over-utilization.
Global secondments, rotational programs and remote project assignments further helped develop talent into versatile generalists while advancing their international management experience. Carefully curated deployment also promoted knowledge sharing and best practices globally. Annual strategic workforce planning involving business leaders gave direction to the skills EY wanted to build or sustain in priority areas and regions over the next 3-5 years to support growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, establishing a fact-based and goal-oriented HR strategy aligned with business needs that is clearly communicated and properly executed is key to developing an effective HR strategy for the organization.
By following the mentioned steps, HR departments can formulate a comprehensive strategy to attract, develop, and retain talent. Regular reviews allow the strategy to adapt to changing circumstances while maintaining focus on the organization's strategic priorities. With a rigorous yet flexible approach, HR strategies can optimize human capital management and create lasting value for all stakeholders.




